How Do You Decide Between a Short Term and Long Term Electricity Contract?
When choosing between a short-term and long-term electricity contract, consider your needs for price stability and flexibility. Long-term contracts typically offer fixed rates, providing predictable electricity costs and protection from future market price increases. This can be advantageous when electricity prices are low or if budgeting certainty is a priority. On the other hand, short-term contracts offer more flexibility, allowing you to take advantage of potentially lower market prices in the future but carrying the risk of higher costs upon renewal if market rates rise. Your decision should depend on current market conditions, your financial goals, and your comfort level with market fluctuations.
What are Short Term or Month to Month Electricity Contracts?
Short-term electricity supply contracts are usually under a year in length. Some common offerings include six-month, three-month and month-to-month electricity plans. Depending on the plan you choose, your rates in a short-term electricity contract may stay the same or fluctuate based on the market. For example, month-to-month electricity plans are also known as variable-rate plans because the rate you pay may change each month.
With these types of contracts, you’ll need to shop around for new rates more often. This can be a good or bad thing depending on the time of year you start or renew your contract.
The advantages of a short-term electricity contract
Understanding the benefits of short-term vs. long-term electricity contracts will help you figure out which option best fits your needs. The following are some of the advantages of a short-term electricity contract:
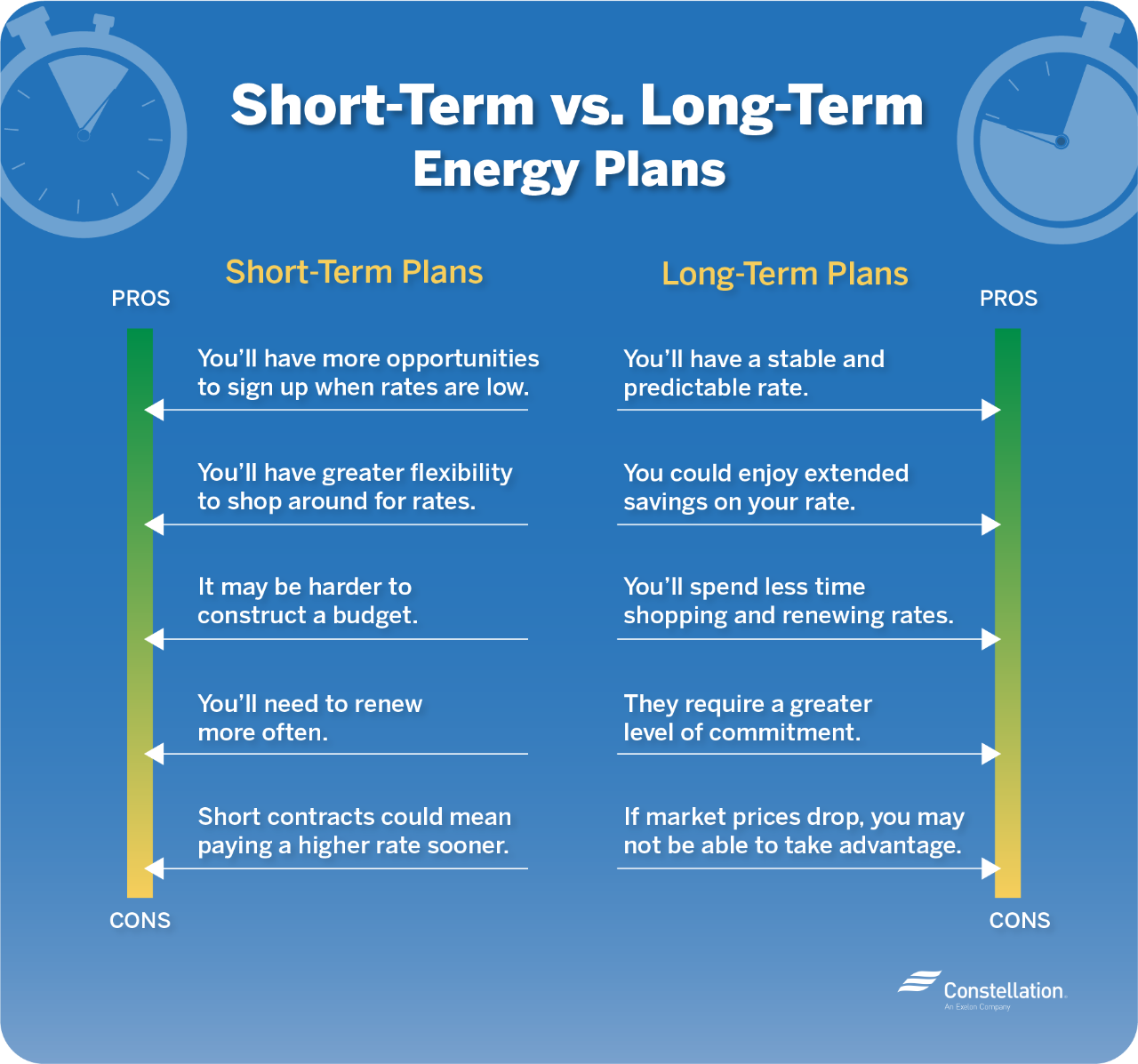
- More opportunities to sign up when rates are low. A month-to-month electricity plan allows you to possibly take advantage of market trends more easily and potentially enter your contract when electricity rates are lowest. By tracking the factors that impact electricity rates, such as which season it is and consumer demand, you may be able to secure a lower rate if market prices are down.
- Greater flexibility. In a short-term electricity contract, you have the flexibility to shop around for lower rates — if they exist — and change plans more frequently. Since they require less commitment than long-term contracts, short-term electricity contracts can be a good option if you move around a lot.
The risks of a short-term electricity contract
Despite the advantages, short-term energy plans also have some drawbacks to consider. Below are some of the risks of a short-term electricity contract:
- Potentially higher rates when renewing. You may enter your month-to-month electricity plan with a low rate, but there’s no guarantee you’ll keep it long. If market prices go up next month, you may get stuck paying a higher rate.
- Need to renew more often. Short-term contracts need to be renewed more often than long-term contracts. This makes it easier to accidentally forget your renewal date.
- Harder to construct a budget. With so many factors affecting market prices, it can be tough trying to predict what your renewal rates will be. This uncertainty makes it difficult to develop a budget with a short-term electricity contract.
What are Long Term Electricity Contracts?
Long-term electricity supply contracts can last from one to five years, or 12 to 60 months. Some of the more common long-term energy plan lengths include 12-month, 24-month and 36-month contracts. These types of electricity contracts usually have rates that remain the same regardless of changes in market prices.
In comparison to short-term contracts, long-term contracts are bigger commitments. But with that commitment comes more stability in your electricity bill each month.
The advantages of a long-term electricity contract
In exchange for a bigger commitment, you can enjoy the benefits of a long-term electricity contract:
- Stable and predictable supply rate. In a long-term contract, you pay a consistent supply rate for the duration of your contract. So, if market rates go up over high-demand seasons, you won’t have to worry about renewing your contract or adjusting your supply rate. This predictability also makes it easier for you to budget your expenses.
- Potential for extended savings. If you enter a long-term electricity contract when rates are low, you’ll keep that rate throughout the duration of your contract. This allows you to potentially save over a long period of time.
- Less time spent shopping and renewing rates. Another benefit of long-term electricity contracts is that you won’t have to shop for rates and renew your contract as often as you would in a short-term contract. This saves you the time and hassle of having to regularly compare electricity supply rates.
The downsides of a long-term electricity contract
Although the stability of a long-term contract is nice, there are some disadvantages to these types of plans. The following are some downsides of a long-term electricity contract:
- Can’t take advantage when market prices drop. In a long-term electricity contract, you’ll have fewer opportunities to shop around for new rates without breaking your contract. This lack of flexibility means you may be stuck with a higher rate if market prices drop.
- Greater level of commitment. Long-term electricity contracts can last up to 60 months, so they require greater commitment than short-term contracts. This means more difficulty (and possibly penalty fees) changing rates or switching energy providers mid-contract if you’re unhappy with your supply service.